SQL
Contents
FUNCTION
To provide direct SQL commands. This statement has been introduced into Jazz
to facilitate Easytrieve Conversion, but it is also available for general Jazz
programming.
FORMAT
SQL UPDATE Table
SET Column = Value [,Column =
Value]…
{WHERE Condition | ALLROWS} [NOCHECK];
Or
SQL DELETE Table
{WHERE Condition | ALLROWS} [NOCHECK];
Or SQL
{COMMIT | ROLLBACK} [NOCHECK];
FUNCTION
SQL UPDATE will update the selected rows with the values given in the SET option.
SQL DELETE will delete the selected rows
SQL COMMIT immediately ensures that all changes that have been made to the database are committed, so they will be available to other users even if your program later abends.
SQL ROLLBACK rolls back all changes to the database since the previous commit.
NOCHECK option.
Unless option NOCHECK is present, SQL UPDATE and SQL DELETE are automatically checked for success (SQLCODE = 0 or 100), and a message is produced if the operation is unsuccessful. SQLCODE = 100 signifies “No Data”, i.e. the WHERE clause found no records. If you want to distinguish this situation, you can add logic
IF SQLCODE = 100;
…
END IF;
NOCHECK can be specified with SQL COMMIT and SQL ROLLBACK , but there is no automatic checking
with these options so it is ignored.
You will
usually specify NOCHECK if you’re
converting an EZT program that includes explicit SQLCODE checks.
Note that
Jazz does not provide
SQL SELECT
Instead, if
you want to process several rows, write something like: -
PROCESS Table WHERE condition [UPDATE]
Program logic that may
change the values of one or more columns
END PROCESS Table [UPDATE];
See https://www.jazzsoftware.co.nz/Docs/JazzLRM_PROCESS.htm
for more information.
To get a
single row, use similar code with GET instead
of PROCESS.
See https://www.jazzsoftware.co.nz/Docs/JazzLRM_GET.htm
Note: if your program contains PROCESS or GET statements that update SQL tables, the generated COBOL logic will already have COMMIT and ROLLBACK statements. It executes a COMMIT when the program ends normally, and ROLLBACK if the program ends abnormally.
Enabling
SQL
SQL statements require that SQL is enabled (Configure/COBOL, [ü] Allow SQL must be checked), and the PROGRAM statement must contain a suitable DATABASE option, e.g.
PROGRAM CLSCHED BATCH DATABASE sample DB2;
If these conditions are met then you can write Jazz programs using SQL,
and generate COBOL. To compile the
COBOL program, you must set its properties to enable SQL.
1. If Jazz is configured to use zOS,
this will be handled automatically with a suitable parameter being included in
the Compile-step JCL.
2. If Jazz is configured to use Rocket Enterprise Suite
(previously Microsoft Enterprise Developer), when you add this program to your
COBOL project,
a.
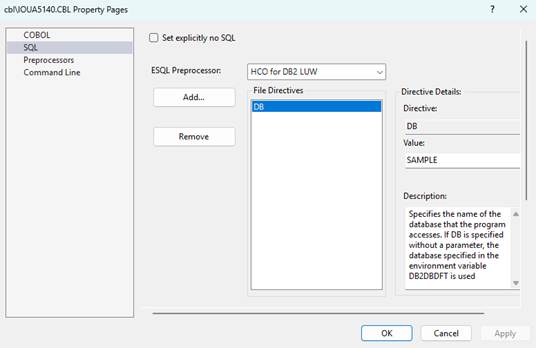
right-click
the COBOL and select Properties
b.
Click
the SQL tab
c.
Add the
database name (“Sample” in my examples) to the DB parameter
SQL Statement Rules
For SQL UPDATE and SQL DELETE the SQL statement names a table. This is the name of a “file” with FileType SQL, and must be defined in the Jazz program, probably included from a COPY statement.
SET defines one or several assignments separated by commas. Each assignment has the form
Column = Value
Column is a field name defined within Table
Value may either be a constant, or a field that is not defined within Table
WHERE defines a condition for the rows that will be updated or deleted. This option is compulsory unless you have written ALLROWS. ALLROWS is provided for situations where you really do mean to update (or delete) all the rows in the table. It is not automatically inserted if WHERE is missing: the role of ALLROWS is to prevent accidental errors, as whole-table updates or deletes could be catastrophic if you didn’t mean to do this.
SQL statements, particularly SQL COMMIT and SQL ROLLBACK, should not be written where a Cursor might be open. For example,
PROCESS CL-SCHED SID(20);
SQL UPDATE CL-SCHED SET CL-SCHED.DAY = 1 WHERE CL-SCHED.CLASS-CODE
= '553:MJA';
SQL COMMIT;
PRINT
(CL-SCHED.*) ;
END PROCESS CL-SCHED;
CL-SCHED is defined DEFINE CL-SCHED SQL DATA(… so the above PROCESS statement reads every record from CL-SCHED with a cursor. The first iteration works correctly, but the SQL COMMIT statement closes the cursor, so the 2nd iteration fails with SQLCODE = 501. This is treated as Endfile, causing the loop to be terminated. The correct way to write this program is to move the two SQL statements out of the PROCESS loop: -
SQL UPDATE CL-SCHED SET CL-SCHED.DAY = 1 WHERE CL-SCHED.CLASS-CODE
= '553:MJA';
SQL COMMIT;
PROCESS CL-SCHED SID(20);
PRINT
(CL-SCHED.*) ;
END PROCESS CL-SCHED;
The PRINT statement produces identical results whether SQL COMMIT is present or not: because the PROCESS loop reads a SQL table, the program will execute SQL COMMIT if it ends normally, and SQL ROLLBACK if it ends abnormally. Writing SQL COMMIT as here is unnecessary.
Names with Hyphens
In SQL, tables and field names
may be named with _, e.g. in the IBM Sample database there is a table called
CL_SCHED, that has fields CLASS_CODE, DAY, STARTING, and ENDDING. CL_SCHED and CLASS_CODE are invalid names in
COBOL, so Jazz and COBOL use hyphens, naming them CL-SCHED and CLASS-CODE. In Jazz SQL statements you write statements
like this, using the name with a hyphen: -
SQL
UPDATE CL-SCHED
SET CL-SCHED.DAY
= 1 WHERE CL-SCHED.CLASS-CODE
= '553:MJA';
However,
names with hyphens are illegal with SQL.
When [PROCESS] converts this to COBOL, it becomes an EXEC SQL … END-EXEC statement. Everything between EXEC SQL and END-EXEC will
use SQL formats, with _ replacing - when referring to SQL Columns and Fields.
003460 EXEC SQL UPDATE CL_SCHED SET CL_SCHED.DAY=1 WHERE CLSCHED
003470 CL_SCHED.CLASS_CODE = '044:HD' END-EXEC. CLSCHED
This example uses a constant value in WHERE CL_SCHED.CLASS_CODE = '044:HD. This example uses a field value: -
DEFINE W DATA(
CLASS-CODE
CHAR(6) VALUE '044:HD');
SQL UPDATE CL-SCHED SET CL-SCHED.DAY = 1 WHERE CL-SCHED.CLASS-CODE =
W.CLASS-CODE;
W.CLASS-CODE
is a CHAR(6) variable: -
002560 01 W. CLSCHED
002570
03 CLASS-CODE PIC X(6) VALUE '044:HD'.
CLSCHED
Outside EXEC SQL … END-EXEC both database and other fields are referred to normally, using their names with hyphens and the usual field-name OF record-name format: -
003550 MOVE CLASS-CODE OF W TO CLASS-CODE OF CL-SCHED. CLSCHED
However,
look at the way in which the field is referenced within the EXEC SQL statement.
A leading colon denotes a field reference, and the field reference has the SQL
style Record-name period field-name. The
field name DOES NOT have the hyphen replaced with _: -
003560 EXEC SQL UPDATE CL_SCHED SET CL_SCHED.DAY=1 WHERE CLSCHED
003570 CL_SCHED.CLASS_CODE = :W.CLASS-CODE END-EXEC. CLSCHED